Reviews on AI career
Posted on Jan 15, 2020
To get a better AI job in the future, we should have AI background and some require skills as shown below.
Introduction
Understanding the requirements for different types of AI jobs will help you to better preparing the solid background and skills.
There are five main tasks to develop an AI development life cycles including Data engineering, Modeling, Development, Business analysis and AI infrastructure.
Performing these tasks will based on six basic roles Data scientists, Machine learning engineer, Data analyst, ML-Software engineering, Machine learning researcher and Software engineer.
Specific skills and knowledge
[1] Data engineering
- Strong coding and software engineering skills (especially in machine learning skills)
- Know to use database query languages such as SQL and object-oriented programming languages such as Python, C++, and Java
[2] Modeling
- Language: Python, R, Matlab, C++, Java
- Strong foundations in mathematics, data science, and machine learning.
- Deep learning skills: computer vision, natural language processing, or speech recognition.
[3] Deployment
- Need to write production code, possess strong back-end engineering skills (in Python, Java, C++, and the like)
- Know cloud technologies (for example AWS, GCP, and Azure).
[4] Business analysis
- Solid background on mathematics and data science for analytics
- Soft-skills: communication skills and business acumen.
- Programming languages: R, Python, and Tableau
[5] AI infrastructure
- Software engineering skills to write production code
- Understand cloud technologies.
Summary
Based on the report from WORKERA - a deeplearning.ai company, the list of the required skills below can help you have a good plan to prepare future jobs.
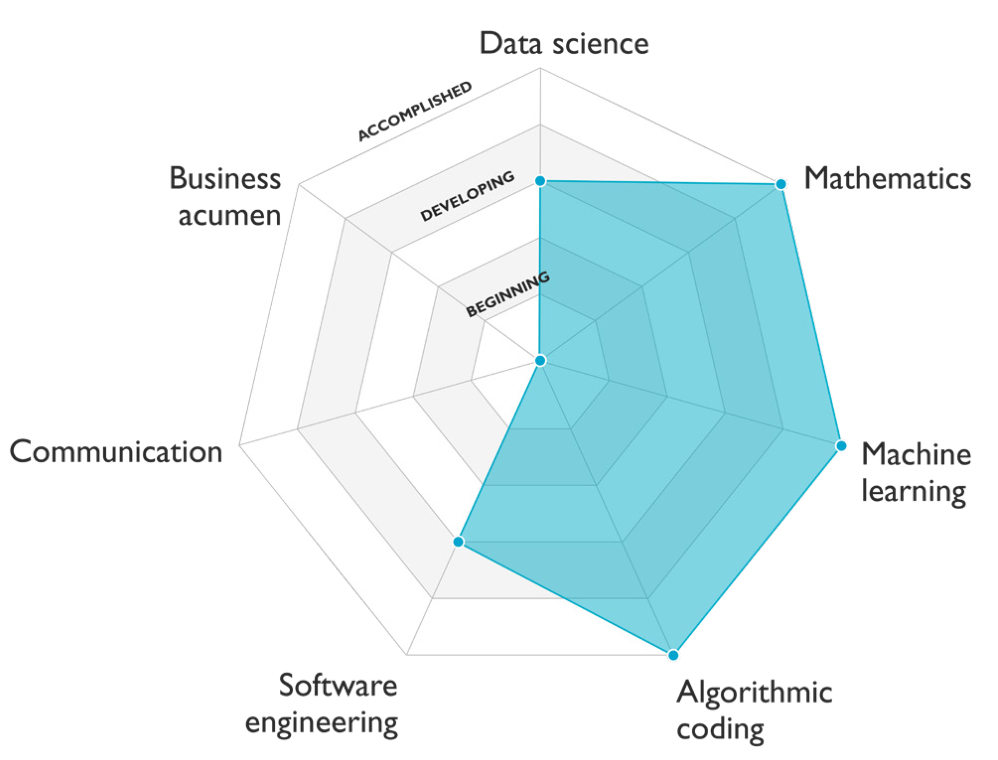
Machine learning
- Understanding classic machine learning models (for example, PCA, K-means, K-NNs, SVM, Logistic Regression, Linear Regression, and Decision Tree learning)
- Methods to train these models (such as initialization, optimization, regularization, and hyperparameter tuning)
- Techniques to strategize machine learning projects.
- Skills
- Tools

Deep learning
- Understanding classic deep learning models (such as fully connected networks, convolutional neural networks, recurrent neural networks, and layers)
- Methods to train these models (such as initialization, regularization, optimization, and transfer learning)
- Techniques to strategize deep learning projects.
Data science
- Knowing to use probabilities (including distributions, conditional probabilities, independence, Bayes theorem, etc.)
- Statistics (including hypothesis testing, bias/variance tradeoffs, mean, variance, and mode)
- Data analysis (including preprocessing, visualization and metrics such as accuracy, R-squared, residuals, precision, and recall).
Mathematics
- Linear algebra (for instance, matrix vector operations, eigenvalues, eigenvectors, and combinatorics)
- Calculus (derivatives, integrals,…)
- Mathematical functions (simple functions, min/max/argmin/argmax, …).
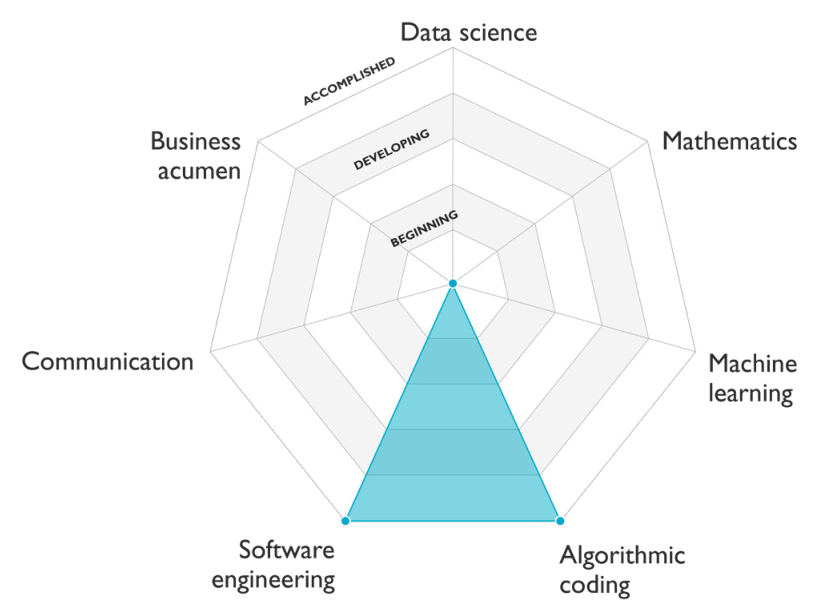
Algorithmic coding
- Understand algorithms written with code, implement classic algorithms like sorting and search.
- Use classic data structures like trees, dictionaries and arrays.
Software engineering
- Having ability to use a variety of computer science and software methods such as object-oriented programming, internet protocols, HTTP requests, agile/scrum methodologies, databases, version control (such as Git), containers, and unit testing.
-
Skills
- Tools

References
[1] WORKERA - Deeplearning.ai company
[2] https://dev.to/patferraggi/planning-my-career-development-for-2020-4okc